What is Additive Manufacturing?
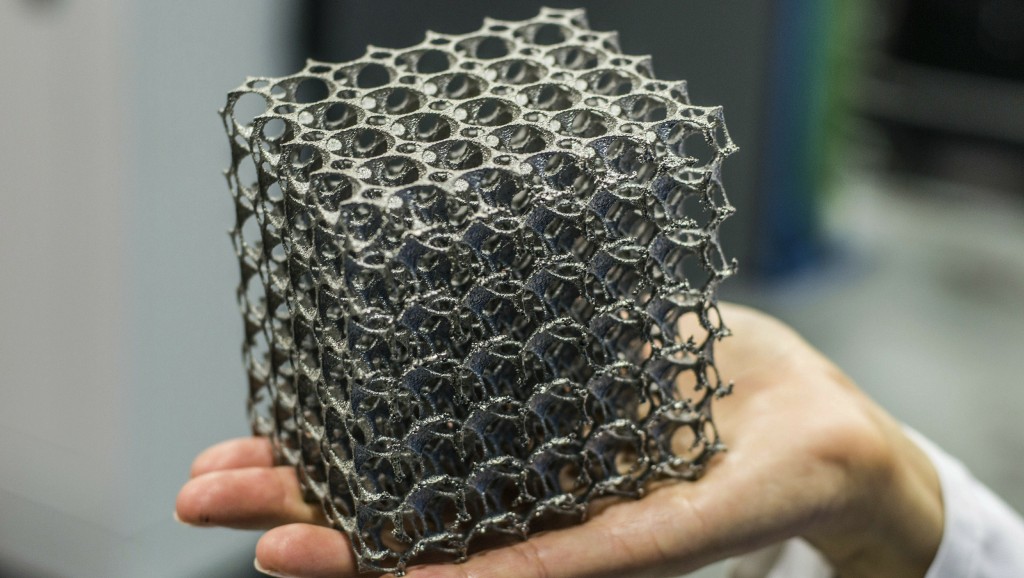
Additive Manufacturing (AM), also known as 3D printing, refers to a manufacturing process, which creates 3D objects by adding multiple layers of material to form components, parts or products. There are various methods of AM, which use a variety of materials such as plastics, glass, ceramics and metal.
Selective laser sintering (SLS) or selective laser melting (SLM) are processes which can be used with a high-powered laser to form 3D objects from metal powders, such as titanium, aluminium, stainless steel and others. SLS fuses metal powder together on a molecular level, allowing for the porosity and other properties of the finished object to be customised, whereas SLM melts the powder together to form the 3D object.
There are many advantages of opting for AM over conventional manufacturing processes. 3D objects can be formed in such a way that traditional manufacturing processes cannot achieve. For example the creation of unique, intricate and sometimes miniature components is easily achieved, for a multitude of applications including industrial, medical, automotive and aerospace to name a few.
The AM process of SLS and SLM requires an inert atmosphere to be used within the laser forming chamber for two reasons; to reduce oxidisation and minimise any impairment of component quality, and to eliminate any chance of the powdered metal igniting together with the presence of any oxygen.
Cambridge Sensotec has been working with leading AM machine manufacturers for many years to supply an extremely reliable oxygen analysis solution. The Rapidox 2100 oxygen analyser has proven to be a reliable instrument for providing the low ppm analysis required for such an application.
For further information about gas analysis or the Rapidox range of gas analysers, please contact us on +44 (0)1480 462142 or email info@cambridge-sensotec.co.uk. Additional information can be found on our website www.cambridge-sensotec.co.uk.